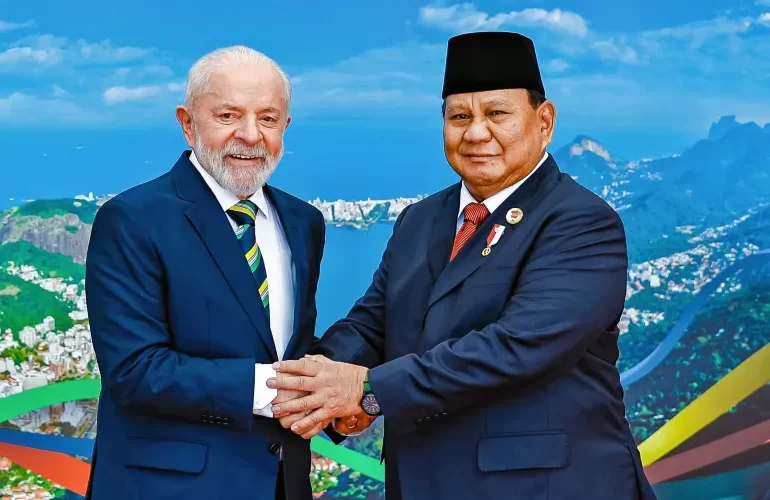
Indonesia Joins BRICS: A Transformative Step Toward Global South Solidarity
Indonesia, the largest economy in Southeast Asia and a prominent player on the global stage, has recently made headlines by joining the BRICS bloc, a coalition of emerging economies originally composed of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. This historic move signals a new chapter in the geopolitical landscape and highlights the growing influence of the Global South in shaping the future of international relations and economic cooperation.
The BRICS bloc, established in 2009, has evolved from a loose grouping of fast-growing economies into a platform for promoting multilateralism, sustainable development, and economic reform. Indonesia’s inclusion in this bloc underscores its rising global stature and the bloc’s expanding reach. This article explores the implications of Indonesia’s membership, its motivations, and the potential impact on regional and global dynamics.

Why Indonesia? The Strategic Importance
Indonesia’s ascension to BRICS is a reflection of its strategic significance. As the fourth most populous country in the world, Indonesia boasts a population of over 270 million and a GDP of approximately $1.3 trillion, making it the largest economy in Southeast Asia. Its location along vital maritime trade routes further enhances its geopolitical importance.
Indonesia’s economy has demonstrated remarkable resilience and growth, driven by a diverse industrial base, abundant natural resources, and a burgeoning digital economy. Moreover, its leadership role within ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) positions it as a bridge between BRICS and the wider Asia-Pacific region. By joining BRICS, Indonesia seeks to amplify its voice on global issues and foster greater economic collaboration with other emerging powers.

Motivations Behind Indonesia’s Decision
Several factors contributed to Indonesia’s decision to join BRICS. First, the bloc’s focus on reshaping the global financial architecture aligns with Indonesia’s aspirations for a more equitable and multipolar world order. BRICS has been advocating for reforms in international institutions such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank, where emerging economies often feel underrepresented.
Second, membership in BRICS offers Indonesia access to a platform for economic cooperation and investment opportunities. The New Development Bank (NDB), established by BRICS, provides an alternative source of funding for infrastructure and sustainable development projects. Indonesia’s participation could attract much-needed investment to support its ambitious infrastructure agenda.
Third, Indonesia’s membership reflects its desire to diversify its economic and diplomatic partnerships. While maintaining strong ties with traditional Western allies, Indonesia aims to strengthen relations with fellow Global South nations to enhance its resilience against external economic shocks and geopolitical tensions.

Expanding the BRICS Bloc: A New Era
Indonesia’s entry into BRICS marks a significant expansion of the bloc. In recent years, BRICS has expressed interest in broadening its membership to include other influential emerging economies. Indonesia’s inclusion is a testament to this strategy, signaling the bloc’s commitment to becoming a more inclusive and representative coalition.
With Indonesia’s membership, BRICS now covers an even larger share of the global population and economic output. This expansion strengthens the bloc’s bargaining power on the international stage and enhances its ability to advocate for reforms in global governance. Furthermore, Indonesia’s participation could pave the way for other ASEAN nations to consider joining BRICS, further integrating Southeast Asia into the bloc’s framework.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Indonesia’s membership in BRICS presents numerous opportunities, it also comes with challenges. One of the primary concerns is managing the diverse interests and priorities of member states. BRICS comprises countries with varying political systems, economic structures, and regional agendas. Ensuring cohesion and consensus among such a diverse group will require skillful diplomacy.
Another challenge lies in balancing Indonesia’s commitments to BRICS with its role in ASEAN. Indonesia has traditionally been a driving force behind ASEAN’s efforts to maintain neutrality and regional stability. Its membership in BRICS could raise questions about its ability to uphold this role without compromising ASEAN’s core principles.
Despite these challenges, Indonesia’s inclusion in BRICS offers significant opportunities. The bloc provides a platform for Indonesia to amplify its voice on global issues such as climate change, trade, and digital transformation. Additionally, Indonesia can leverage its membership to foster closer economic ties with other BRICS nations, particularly in areas like energy, technology, and infrastructure.
Regional and Global Implications
Indonesia’s membership in BRICS is likely to have far-reaching implications for both regional and global dynamics. In Southeast Asia, Indonesia’s participation in the bloc could inspire other nations to explore deeper engagement with BRICS, potentially reshaping the region’s economic and political landscape.
On a global scale, Indonesia’s entry into BRICS reinforces the bloc’s role as a counterbalance to Western-dominated institutions. By bringing together a diverse group of emerging economies, BRICS can advocate for a more inclusive and multipolar world order. Indonesia’s membership also enhances the bloc’s legitimacy and credibility, given its status as a democratic nation with a track record of constructive international engagement.
Furthermore, Indonesia’s inclusion highlights the growing influence of the Global South in shaping the future of international relations. As emerging economies continue to rise, their collective voice will play a crucial role in addressing global challenges and promoting sustainable development.

The Road Ahead
As Indonesia begins its journey as a member of BRICS, it faces the task of navigating a complex and dynamic global landscape. Its membership in the bloc represents an opportunity to strengthen its position as a leader among emerging economies and a champion of multilateralism.
To maximize the benefits of its membership, Indonesia will need to actively engage with other BRICS nations to identify areas of mutual interest and cooperation. It must also ensure that its participation in the bloc complements its commitments to ASEAN and other international forums.
Indonesia’s inclusion in BRICS is a milestone not only for the nation but also for the broader Global South. It underscores the importance of collaboration and solidarity among emerging economies in addressing shared challenges and shaping a more equitable and inclusive world order. As BRICS continues to expand and evolve, Indonesia’s role within the bloc will be instrumental in driving its vision and objectives forward.
In conclusion, Indonesia’s membership in BRICS represents a transformative step toward greater global South solidarity and a more balanced global order. It is a testament to Indonesia’s rising influence and its commitment to fostering economic growth, sustainable development, and multilateral cooperation. As the world watches this historic development unfold, the potential for a more inclusive and equitable future has never been more promising.










